Comparative Study of Convolutional Neural Network Architectures for Automated Classification of Leukemia in Blood Smear Images
Studi Perbandingan Arsitektur Jaringan Syaraf Tiruan Konvolusional untuk Klasifikasi Otomatis Leukemia pada Citra Apusan Darah
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21070/joincs.v8i2.1677Keywords:
classification, ResNet50, ViT Hybrid.Abstract
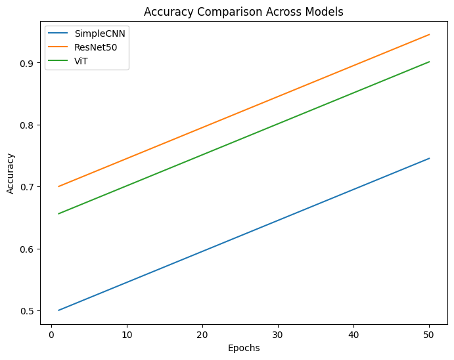
. Microscopic analysis of peripheral blood smears remains a critical and complex step in leukemia diagnosis, which could greatly benefit from automation using deep learning. In this paper, we compare three different deep learning models for automated classification of leukemia cells: a simple CNN, a ResNet, and a hybrid vision transformer. The Kaggle leukemia image dataset, which includes 15,135 blood smear images, was used. The blood smear images were preprocessed using denoising, normalization, upscaling, and upscaling. Training was performed on high-performance GPUs and evaluated on multiple complex metrics such as F-score, precision, recall, and accuracy. The expected outcomes include identifying the most robust and accurate deep learning model for leukemia classification, providing insights into the strengths and weaknesses of different leukemia subtypes, and demonstrating strategies and the effectiveness of image distortion handling. The results showed that ViT Hybrid models outperformed CNN and ResNet, achieving 89% of accuracy, 88% of precision, 90% of recall, and 89% of F-score.This suggests that hybrid structures hold great promise for improving computer-aided diagnosis in hematology. These findings are expected to contribute significantly to the field of medical image analysis, offering an accurate and scalable diagnostic tool with immediate clinical application.
References
[1] R. C. P. P. Sowmiya, S. Yogasundari, S. Kaviya, “Hemo Detect Advancing Hematologic Health through Automated Leukemia Detection,” Int. Conf. Mod. Trends Eng. Manag., 2024, doi: 10.59544/jckd6637/icmtem24p5.
[2] C. Hassan Abbas Gondal et al., “Automated Leukemia Screening and Sub-types Classification Using Deep Learning,” Computer Systems Science and Engineering, vol. 46, no. 3. pp. 3541–3558, 2023. doi: 10.32604/csse.2023.036476.
[3] R. Baig, A. Rehman, A. Almuhaimeed, A. Alzahrani, and H. T. Rauf, “Detecting Malignant Leukemia Cells Using Microscopic Blood Smear Images: A Deep Learning Approach,” Appl. Sci., vol. 12, no. 13, 2022, doi: 10.3390/app12136317.
[4] P. K. Das, V. A. Diya, S. Meher, R. Panda, and A. Abraham, “A Systematic Review on Recent Advancements in Deep and Machine Learning Based Detection and Classification of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia,” IEEE Access, vol. 10, no. July, pp. 81741–81763, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3196037.
[5] S. Singla, “Convolutional Neural Network-Based Approach for Classification of Blood Cells in Leukaemia Detection,” IEEE, 2024, doi: 10.1109/ICoICI62503.2024.10695974.
[6] andPhilip I. Ibomoiye Domor Mienye , Theo G. Swart , George Obaido , Matt Jordan, “Deep Convolutional Neural Networks in Medical Image Analysis: A Review Ibomoiye.” 2025. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/info16030195.
[7] O. G. and L. Wilcox, “Developing Deep Learning Models for Classifying Medical Imaging Data.” 2025. doi: 10.20944/preprints202506.1420.v1.
[8] M. G. & B. O. S. Shilpa Choudhary, Sandeep Kumar, Pammi Sri Siddhaarth, Guntu Charitasri, Monali Gulhane, Nitin Rakesh, Feslin Anish Mon, Amal Al-Rasheed, “Advancing blood cell detection and classification: performance evaluation of modern deep learning models.” pp. 2–22, 2025. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-025-03027-2.
[9] S. J. Mohaiminul Islam, Guorong Chen, “An Overview of Neural Network,” Am. J. Neural Networks Appl., vol. 5, no. 1, 2019, doi: 10.11648/j.ajnna.20190501.12.
[10] P. D. ́AR M ́at ́e HIRE ˇS, Peter BUGATA, Matej GAZDA, D ́avid J. HRE ˇSKO, R ́obert KAN ́ASZ, Luk ́aˇs VAVREK, “Brief Overview of Neural Networks for Medical Applications,” Acta Electrotech. Inform., vol. 22, p. 2, 2022, doi: 10.2478/aei-2022-0010.
[11] D. T. Shervin Minaee, Yuri Boykov, Fatih Porikli, Antonio Plaza, Nasser Kehtarnavaz, “Image Segmentation Using Deep Learning: A Survey,” Intell. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach., vol. 44, no. 7, 2021, doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3059968.
[12] A. R. M. BHARADWAJ MANDA , PRANJAL BHASKARE, “A Convolutional Neural Network Approach to the Classification of Engineering Models,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3055826.
[13] M. Baylor, D., Breck, E., Cheng, H. T., Fiedel, N., Foo, C. Y., Haque, Z., Haykal, S., Ispir, M., Jain, V., Koc, L. K., Koo, C. Y., Lew, L., Mewald, C., Modi, A. N., Polyzotis, N., Ramesh, S., Roy, S., Whang, S. E., & Zinkevich, “TFX: A TensorFlow-Based Production-Scale Machine Learning Platform,” ACM SIGKDD Int. Conf. Knowl. Discov. Data Min. (KDD ’17), pp. 1387–1395, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/3097983.309802.
[14] A. T. Marinela Branescua , Stephen Swifta, “A Comparison of Convolutional Neural Networks and Traditional Feature-Based Classification Applied to Leukaemia Image Analysis,” Stud Heal. Technol Inf., vol. 29;, no. 295, pp. 545–550, 2022, doi: 10.3233/SHTI220786.
[15] K. A. Kadhim, F. H. Najjar, A. A. Waad, I. H. Al-Kharsan, Z. N. Khudhair, and A. A. Salim, “Leukemia Classification using a Convolutional Neural Network of AML Images,” Malaysian J. Fundam. Appl. Sci., vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 306–312, 2023, doi: 10.11113/mjfas.v19n3.2901.
[16] T. N. and N. S. N. Gokulkrishnan, “Deep Learning-Based Analysis of Blood Smear Images for Detection of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia,” IEEE Int. Conf. Electron. Comput. Commun. Technol., pp. 1–5, 2023, doi: 10.1109/CONECCT57959.2023.10234824.
[17] A. Badruzzaman and A. M. Arymurthy, “A Comparative Study of Convolutional Neural Network in Detecting Blast Cells for Diagnose Acute Myeloid Leukemia,” Journal of Electronics, Electromedical Engineering, and Medical Informatics, vol. 6, no. 1. pp. 84–91, 2024. doi: 10.35882/jeeemi.v6i1.354.
[18] R. B. J Senthil Kumar, “A Novel Approach for Leukemia Classification using Multi-Neural Networks,” Int. Conf. Cogn. Robot. Intell. Syst. (ICC - ROBINS), pp. 340–345, 2024, doi: 10.1109/ICC-ROBINS60238.2024.10534018.
[19] M. Claro, B. Departamento de Computação, Universidade Federal do Piauí, Teresina, and ; Luis Vogado; Rodrigo Veras; André Santana; João Tavares; Justino Santos; Vinicius Machado, “Convolution Neural Network Models for Acute Leukemia Diagnosis,” Int. Conf. Syst. Signals Image Process., 2020, doi: 10.1109/IWSSIP48289.2020.9145406.
[20] U. Agustin, R.I., Arif, A. & Sukorini, “Classification of immature white blood cells in acute lymphoblastic leukemia L1 using neural networks particle swarm optimization,” Neural Comput Applic, vol. 33, pp. 10869–10880, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06245-7.
[21] A. K.K. and M. V.J.v, “Automated Detection of B Cell and T Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Using Deep Learning,” Irbm, vol. 43, no. 5, pp. 405–413, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irbm.2021.05.005.
[22] S. D. Snehal Laddha, “Analysis of White Blood Cell Segmentation Techniques and Classification Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Leukemia Detection,” HELIX, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 4519-4524 DOI, 2018, doi: 10.29042/2018-4519-4524.
[23] M. S. Alkhouli and H. Joshi, “Performance Analysis for Optimized Light Weight CNN Model for Leukemia Detection and Classification using Microscopic Blood Smear Images,” Scalable Comput. Pract. Exp., vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 1716–1727, 2024, doi: 10.12694/scpe.v25i3.2798.
[24] M. Z. Ullah et al., “An attention-based convolutional neural network for acute lymphoblastic leukemia classification,” Appl. Sci., vol. 11, no. 22, 2021, doi: 10.3390/app112210662.
[25] T. P. T. A. and H.-C. K. Rakhmonalieva Farangis Oybek Kizi, “A Review of Deep Learning Techniques for Leukemia CancerClassification Based on Blood Smear Images.” 2025. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci4010009.
[26] A. Awad and S. A. Aly, “Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Diagnosis Employing YOLOv11,YOLOv8, ResNet50, and Inception-ResNet-v2 Deep Learning Models.” 2025. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2502.09804
[27] D. P. Y. and A. D. D. Vishesh Tanwar , Bhisham Sharma, “Enhancing Blood Cell Diagnosis Using Hybrid Residual and Dual Block Transformer Network.” 2025. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020098.
[28] L. . Al-Bashir, A.K., Khnouf, R.E. & Bany Issa, “Leukemia classification using different CNN-based algorithms-comparative study,” Neural Comput. Appl., vol. 36, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-09554-9.
[29] K. K. A. A, V.J. Manoj, and T. M. Sagi, “Automated detection of leukemia by pretrained deep neural networks and transfer learning: A comparison,” Med. Eng. Phys., vol. 98, pp. 8–19, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2021.10.006.
[30] K. A. P. Preethika, “Hybrid Vision Transformer and CNN for Leukemia Detection in Blood Smear Images,” 2025 11th Int. Conf. Commun. Signal Process. (ICCSP),Melmaruvathur, India, pp. 1344–1349, 2025, doi: 10.1109/ICCSP64183.2025.11088481.
[31] B. R. et Al., “A Cutting-Edge Ensemble of Vision Transformer and ResNet101v2 Based Transfer Learning for the Precise Classification of Leukemia Sub-types from Peripheral Blood Smear Images,” Int. Conf. Electr. Eng. Inf. Commun. Technol., pp. 49–54, 2024, doi: 10.1109/ICEEICT62016.2024.10534388.
[32] M. Abou Ali, F. Dornaika, and I. Arganda-Carreras, “White Blood Cell Classification: Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Vision Transformer (ViT) under Medical Microscope,” Algorithms, vol. 16, no. 11, 2023, doi: 10.3390/a16110525.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Marwa Raid Hameed

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





