A Robust Hybrid CNN–LSTM Framework for High-Accuracy Zero-Day Intrusion and Ransomware Detection Using the UGRansome Dataset
A Robust Hybrid CNN–LSTM Framework for High-Accuracy Zero-Day Intrusion and Ransomware Detection Using the UGRansome Dataset
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21070/joincs.v9i1.1688Keywords:
Intrusion Detection System, Ransomware, Zero-Day Attacks, CNN–LSTM, Deep Learning, UGRansome Dataset, Cybersecurity, SMOTEAbstract
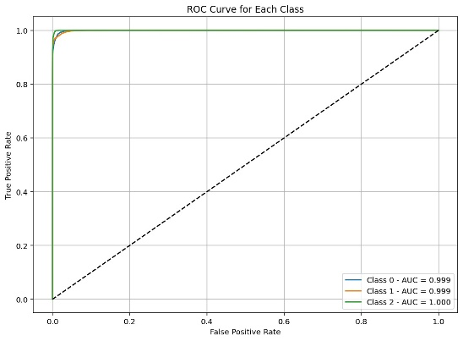
The rapid evolution of cyber-attacks—particularly zero-day intrusions and ransomware—has intensified the need for intelligent and resilient detection systems capable of handling imbalanced, high-dimensional network traffic. This research proposes a robust hybrid deep learning framework combining Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks for enhanced anomaly detection using the UGRansome dataset, a realistic benchmark designed for ransomware and zero-day behavior analysis. The methodology integrates advanced preprocessing, including categorical encoding, feature normalization, and Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE) to alleviate class imbalance. The hybrid architecture leverages CNN layers for spatial feature extraction and LSTM layers for modeling temporal dependencies, enabling improved detection of emerging and stealthy threats. Experimental results demonstrate superior performance compared to standalone deep learning baselines, achieving 97.89% accuracy, 0.999 macro AUC, and strong detection capability across minority classes. Confusion matrix visualizations and classification metrics confirm the model’s robustness and generalization. The findings highlight the potential of hybrid deep learning models for proactive cybersecurity defense and establish a foundation for future intelligent intrusion detection systemsReferences
1. L. Mohammadpour, “A Survey of CNN-Based Network Intrusion Detection,” Applied Sciences, vol. 12, no. 16, 8162, 2022.
2. K. Zhang, Y. Wang, U. Bhatti, Y. Zhou, and M. Jin, “Enhanced ransomware attacks detection using feature selection, sensitivity analysis, and optimized hybrid model,” Journal of Big Data, 2025.
3. Md. A. Rahman and S. M. R. H. Nijhum, “Recurrent Neural Network Based Hybrid Deep Learning Architecture for Enhanced Network Intrusion Detection,” in Proc. PEEIACON, 2024, pp. 400–405.
4. Y. Wang, “Deep Learning-Based Network Intrusion Detection Systems,” Applied and Computational Engineering, vol. 109, no. 1, pp. 179–188, 2024.
5. B. Wang, Y. Su, M. Zhang, and J. Nie, “A Deep Hierarchical Network for Packet-Level Malicious Traffic Detection,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 201728–201740, 2020.
6. J. Yin, B. Hou, J. Dai, and Y. Zu, “A CNN-BiLSTM Method Based on Attention Mechanism for Class-Imbalanced Abnormal Traffic Detection,” 2024.
7. N. Elsayed, Z. S. Zaghloul, S. W. Azumah, and C. Li, “Intrusion Detection System in Smart Home Network Using Bidirectional LSTM and Convolutional Neural Networks Hybrid Model,” 2021. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.12096
8. I. Shivhare, J. Purohit, V. Jogani, S. Attari, and M. Chandane, “Intrusion Detection: A Deep Learning Approach,” 2023. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.07601
9. A. Gueriani, H. Kheddar, and A. C. Mazari, “Enhancing IoT Security with CNN and LSTM-Based Intrusion Detection Systems,” 2024.
10. The Age of Ransomware: A Survey on the Evolution, Taxonomy, and Research Directions, IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 40698–40723, 2023.
11. Z. H. Mohammed, F. H. Khorsheed, and G. J. Ahmed, “Ensemble Deep Learning Strategy for Handling Imbalanced Credit Card Fraud Data,” JOINCS (Journal of Informatics, Network, and Computer Science), vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 94–105, 2025.
12. R. Su, Generative Mathematical Models for Ransomware Attack Prediction, 2025.
13. A. Alsmadi, et al., “A Self-Adaptive Intrusion Detection System Using Deep Q-Networks,” 2025.
14. J. Yan, et al., “Ransomware Detection Using Hybrid Deep Learning,” 2024.
15. M. Tokmak and M. Nkongolo, “Stacking an Autoencoder for Feature Selection in Ransomware Detection,” 2024.
16. M. Tokmak, Zero-Day Threats Detection for Critical Infrastructures, 2023.
17. S. Chaudhary and A. Adhikari, “Ransomware Detection Using Machine Learning Techniques,” 2024.
18. P. Azugo, H. Venter, and R. Nkongolo, “Ransomware Detection Using the UGRansome2024 Dataset,” 2024.
19. S. R. Zahra, “Optimal Approach for Anomaly Intrusion Detection Using Ensemble Learning,” 2022.
20. R. Nkongolo, et al., “UGRansome1819: A Novel Dataset for Anomaly Detection and Zero-Day Threats,” 2021. M. Wa Nkongolo, "UGRansome Dataset." Kaggle, https://doi.org/10.34740/KAGGLE/DSV/7172543.
21. M. Tokmak, "Deep Forest Approach for Zero-Day Attacks Detection," in Innovations and Technologies in Engineering, S. Tasdemir and I. Ali Ozkan, Eds. Istanbul, Turkey: Eğitim Yayinevi, 2022.
22. D. Shankar, G. V. Sudha, J. N. S. S. Naidu, and P. S. Madhuri, "Deep Analysis of Risks and Recent Trends Towards Network Intrusion Detection System," International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 262-276, 2023, https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2023.0140129.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Farah Hatem Khorsheed, Enas Abbas Abed , Zainab Hassan Mohammed , Walaa Badr Khudhair Alwan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





